内容目录
1、 概览
这是一个个人对LFU缓存算法的设计及实现的讲解。
完整源码地址:github地址
https://github.com/fofcn/operation-system/tree/main/%E5%AE%9E%E8%B7%B5/os/src/main/java/cache/lfu
2、介绍
LFU(Least Frequently Used) 最不经常使用缓存算法。
算法思想是为了确定最不常用的key,可以为缓存中的每个key维护一个计数器,使用技术最小的key就是最不经常使用的缓存算法。
当向容器中添加一个新的Key时,如果缓存已经达到最大容量时,LFU会移除访问频率最小的元素,如果最小频率中有多个元素,那么就移除最早添加到容器的key,这个特性类似LRU。
2.1、LFU的功能
- set 向LFU中添加一个键值对
- get 根据键从LFU中获取一个值,如果没有则返回空
2.2、LFU的特性
- LFU缓存有一个固定大小
- 所有的操作都是O(1)
- 支持并发
- 添加新的key在缓存容量满时会移除一个key
3、LFU的结构设计
3.1、结构设计概览
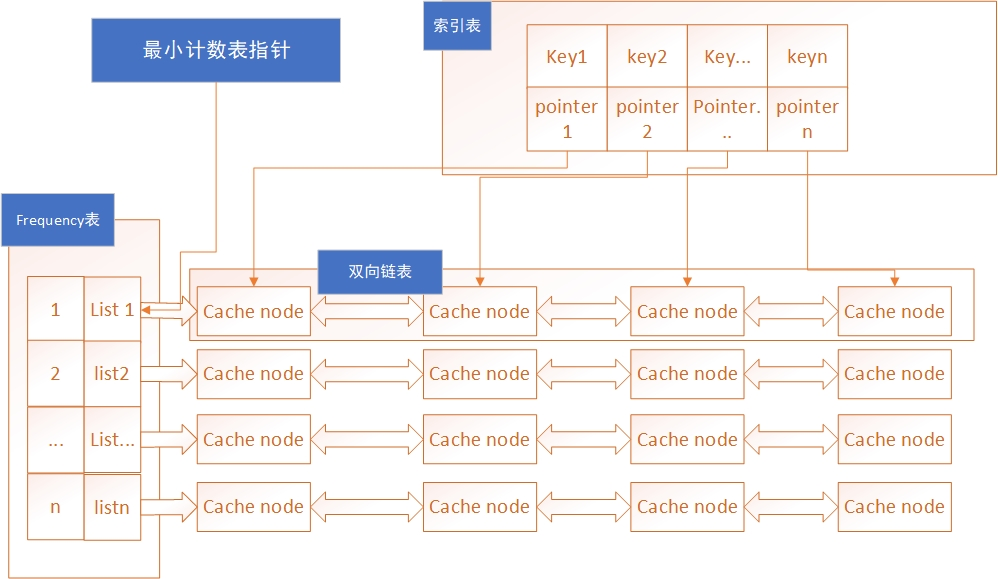
3.2、索引表
为了能够在O(1)时间获取到一个key对应的value,我们需要对键值对设置一个索引,数据结构采用Map
3.3、frequency表
为了能够在O(1)时间内查找到对应计数链表,使用frequency表作为计数的索引。
3.4、最小计数表指针
为了能够在O(1)时间内查找到需要移除的键值对,我们维护一个最小计数链表指针,用于快速定位待删除的计数链表。
3.5、双向链表
为了能够在O(1)时间内删除一个键值对,我们使用链表来管理缓存键值对。
为了能够实现addLast、removeFirst和removeLast操作我们需要使用双向链表。
4、LFU算法
4.1、cache失效
在cache失效时我们需要执行set操作,set操作主要有以下几步:
- 将新节点添加到索引表
- 将新节点添加到frequency表
- 将最小计数表指针指向计数最小的表
- 针对缓存容量满时,根据最小计数表指针删除一个节点
4.2、cache命中
在cache命中时,我们需要执行get操作,get操作主要有以下几步:
- 从索引表中获取节点
- 从frequency表中找到节点,并提升节点的计数,将节点添加到下一计数表中
- 更新最小计数表指针(如果需要更新)
5、Java实现
5.1、接口定义
5.1.1、缓存接口定义
public interface Cache<K, V> {
/**
* 增加缓存
* @param k 缓存key
* @param v 缓存value
*/
void set(K k, V v);
/**
* 从缓存中根据key获取一个值
* @param k 缓存key值
* @return
*/
V get(K k);
/**
* 缓存大小
* @return
*/
int size();
/**
* 缓存全部清空
*/
void clear();
}
5.1.2、缓存节点定义
public class CacheNode<K, V> {
protected K key;
protected V value;
private CacheNode<K, V> prev;
private CacheNode<K, V> next;
public CacheNode(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
public void setKey(K key) {
this.key = key;
}
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(V value) {
this.value = value;
}
public CacheNode<K, V> getPrev() {
return prev;
}
public void setPrev(CacheNode<K, V> prev) {
this.prev = prev;
}
public CacheNode<K, V> getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(CacheNode<K, V> next) {
this.next = next;
}
}
5.1.3、LFU 缓存节点定义
public class LfuCacheNode<K, V> extends CacheNode<K, V> {
private int frequency;
public LfuCacheNode(K key, V value) {
this(key, value, 1);
}
public LfuCacheNode(K key, V value, int frequency) {
super(key, value);
this.frequency = frequency;
}
public int getFrequency() {
return frequency;
}
public void setFrequency(int frequency) {
this.frequency = frequency;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "LfuCacheNode{" +
"frequency=" + frequency +
", key=" + key +
", value=" + value +
'}';
}
}
5.2 Set操作
public void set(K k, V v) {
// 基本参数检查
if (k == null || v == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("K V");
}
lock.lock();
try {
// 尝试从缓存索引表中查找key是否存在
LfuCacheNode<K, V> node = indexTable.get(k);
// 不存在则检查缓存容量是否超过了最大容量
if (node == null) {
// 如果当前缓存节点大小超过了容量,则执行删除
if (size() == capacity) {
evictCacheNode(true);
}
// 新建一个缓存节点并将缓存节点添加到LFU双向链表中
node = new LfuCacheNode<>(k, v);
LfuCacheNodeList list = freqMap.get(node.getFrequency());
if (list == null) {
list = new LfuCacheNodeList(node.getFrequency());
if (first == null || first.getFrequency() != 1) {
first = list;
}
}
// 将缓存节点添加到frequency表中
freqMap.put(node.getFrequency(), list);
node = list.addLast(node);
indexTable.put(k, node);
} else {
// 根据计数获取列表
// 从当前列表中删除
// 如果list的数量为空,从map中删除列表
// 如果list的数量不为空,则不处从map中删除列表
doPromote(k, v, node);
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}set操作关键点主要是容量满了以后删除缓存节点evictCacheNode和提升缓存节点计数doPromote的操作。
5.2.1、提升节点计数实现
private void doPromote(K k, V v, LfuCacheNode<K, V> node) {
// 从frequency表中获取链表,并从链表中删除数据
int frequency = node.getFrequency();
LfuCacheNodeList list = freqMap.get(frequency);
list.remove(node);
// 节点计数更新
node.setFrequency(node.getFrequency() + 1);
// 从下一个frequency表中获取下一个计数列表
LfuCacheNodeList nextList = freqMap.get(node.getFrequency());
// 将节点放入到下一个节点列表
if (nextList == null) {
nextList = new LfuCacheNodeList(node.getFrequency());
}
nextList.addLast(node);
freqMap.put(node.getFrequency(), nextList);
node.setValue(v);
// 前一个frequency表中的链表已经没有数据,那么我们就更新first指针
if (list.size() == 0) {
list.setPrev(null);
list.setNext(null);
freqMap.remove(frequency);
// 更新first指针
// 更新条件: 如果要删除的list==first,则更新first为next
if (list == first) {
first = nextList;
}
}
indexTable.put(k, node);
}5.2.2、删除缓存节点实现
private void evictCacheNode(boolean onlyOne) {
// 直接从最小计数链表中删除第一个
LfuCacheNodeList list = first;
CacheNode node = list.removeFirst();
// 如果删除完成后该计数链表没有缓存节点,则将计数节点删除
// 这里没有更新first,容量满时触发删除节点导致first更新时,说明有计数为1的节点要加入到frequency表
if (list.size() == 0) {
freqMap.remove(list.getFrequency());
}
// 将索引表中的缓存节点删除
indexTable.remove(node.getKey());
}
5.3 get操作
public V get(K k) {
lock.lock();
try {
// 从索引表获取缓存节点
// 如果缓存节点存在那么就提升缓存节点的计数,并将节点添加到下一个计数链表中
LfuCacheNode<K, V> node = indexTable.get(k);
if (node != null) {
doPromote(k, node.getValue(), node);
indexTable.put(k, node);
return node.getValue();
}
return null;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}5.4 测试用例
public class LfuCacheTest {
private LfuCache<Integer, String> lfuCache;
private final int capacity = 2;
// private final String command = "\"LFUCache\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"get\",\"put\",\"get\",\"get\",\"put\",\"get\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"get\",\"put\",\"get\",\"get\",\"get\",\"get\",\"put\",\"put\",\"get\",\"get\",\"get\",\"put\",\"put\",\"get\",\"put\",\"get\",\"put\",\"get\",\"get\",\"get\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"get\",\"put\",\"get\",\"get\",\"put\",\"put\",\"get\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"get\",\"put\",\"put\",\"get\",\"put\",\"put\",\"get\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"get\",\"put\",\"put\",\"get\",\"put\",\"get\",\"get\",\"get\",\"put\",\"get\",\"get\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"get\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"get\",\"get\",\"get\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"get\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"get\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"get\",\"get\",\"get\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"get\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\",\"put\"";
private final String command = null;
// private final String data = "[10],[10,13],[3,17],[6,11],[10,5],[9,10],[13],[2,19],[2],[3],[5,25],[8],[9,22],[5,5],[1,30],[11],[9,12],[7],[5],[8],[9],[4,30],[9,3],[9],[10],[10],[6,14],[3,1],[3],[10,11],[8],[2,14],[1],[5],[4],[11,4],[12,24],[5,18],[13],[7,23],[8],[12],[3,27],[2,12],[5],[2,9],[13,4],[8,18],[1,7],[6],[9,29],[8,21],[5],[6,30],[1,12],[10],[4,15],[7,22],[11,26],[8,17],[9,29],[5],[3,4],[11,30],[12],[4,29],[3],[9],[6],[3,4],[1],[10],[3,29],[10,28],[1,20],[11,13],[3],[3,12],[3,8],[10,9],[3,26],[8],[7],[5],[13,17],[2,27],[11,15],[12],[9,19],[2,15],[3,16],[1],[12,17],[9,1],[6,19],[4],[5],[5],[8,1],[11,7],[5,2],[9,28],[1],[2,2],[7,4],[4,22],[7,24],[9,26],[13,28],[11,26]";
private final String data = null;
private final Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("\\[(\\d+,)?\\d+]");
List<String> funcNameList;
List<String[]> dataList;
@Before
public void before() {
dataList = new ArrayList<>();
if (data != null && !data.isEmpty()) {
int counter = 0;
Matcher m = pattern.matcher(data);
while (m.find()) {
String d = data.substring(m.start(), m.end()).replace("[", "").replace("]", "");
if (counter == 0) {
Integer capacity = Integer.parseInt(d);
lfuCache = new LfuCache<>(capacity);
} else {
String[] inputs = d.split(",");
dataList.add(inputs);
}
counter++;
}
}
funcNameList = new ArrayList<>();
// 解析命令
if (command != null && !command.isEmpty()) {
String[] funcs = command.split(",");
if (funcs != null && funcs.length > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < funcs.length; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
continue;
}
String funcName = funcs[i].replace("\"", "");
if (funcName.equals("put")) {
funcName = "set";
} else if (funcName.equals("get")) {
funcName = "get";
}
funcNameList.add(funcName);
}
}
} else {
StdOut.println("new lfu cache");
lfuCache = new LfuCache<>(capacity);
}
}
@After
public void after() {
lfuCache.clear();
}
@Test
public void testLeetCodeTestCase() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
System.out.println("null");
for (int i = 0; i < funcNameList.size(); i++) {
String funcName = funcNameList.get(i);
String[] arguments = dataList.get(i);
Integer key = Integer.parseInt(arguments[0]);
Object ret = invokeMethod(funcName, key, arguments);
if ("set".equals(funcName)) {
System.out.println(funcName + "->[" + arguments[0] + ", " + arguments[1] + "] ->" + ret);
} else {
System.out.println(funcName + "->[" + arguments[0] + "] ->" + ret);
}
}
}
@Test
public void testSetAndSetLeetCode() {
lfuCache = new LfuCache<>(3);
lfuCache.set(2, "2");
lfuCache.set(1, "1");
String str = lfuCache.get(2);
Assert.assertEquals("2", str);
str = lfuCache.get(1);
Assert.assertEquals("1", str);
str = lfuCache.get(2);
Assert.assertEquals("2", str);
lfuCache.set(3, "3");
lfuCache.set(4, "4");
str = lfuCache.get(3);
Assert.assertNull(str);
str = lfuCache.get(2);
Assert.assertEquals("2", str);
str = lfuCache.get(1);
Assert.assertEquals("1", str);
str = lfuCache.get(4);
Assert.assertEquals("4", str);
}
@Test
public void testSetAndGet() {
lfuCache = new LfuCache<>(2);
// 预期: [frequency = 1]->[[key = 1, value = 1]]
// 实际: {frequency=1}LfuCacheNode{frequency=1, key=1, value=1}
// 结果: 正确
lfuCache.set(1, "1");
// 预期: [frequency = 1]->[[key = 1, value = 1], [key = 2, value = 2]]
// 实际: {frequency=1}LfuCacheNode{frequency=1, key=1, value=1}LfuCacheNode{frequency=1, key=2, value=2}"
// 结果: 正确
lfuCache.set(2, "2");
// 预期:
// [frequency = 1]->[[key = 2, value = 2]]
// [frequency = 2]->[[key = 1, value = 1]]
// 实际:
// {frequency=1}LfuCacheNode{frequency=1, key=2, value=2}
// {frequency=2}LfuCacheNode{frequency=2, key=1, value=1}
// 结果: 正确
String str = lfuCache.get(1);
Assert.assertEquals("1", str);
StdOut.println("get cache from lfucache: key=1, value = " + str);
// 预期:
// [frequency = 1]->[[key = 3, value = 3]]
// [frequency = 2]->[[key = 1, value = 1]]
// 实际:
// {frequency=1}LfuCacheNode{frequency=1, key=3, value=3}
// {frequency=2}LfuCacheNode{frequency=2, key=1, value=1}
// 结果: 正确
lfuCache.set(3, "3");
// 不会改动结构
str = lfuCache.get(2);
Assert.assertNull(str);
StdOut.println("get cache from lfucache: key=2, value = null");
// 预期:
// [frequency = 2]->[[key = 1, value = 1], [key = 3, value = 3]]
// 实际
// {frequency=2}LfuCacheNode{frequency=2, key=1, value=1}LfuCacheNode{frequency=2, key=3, value=3}
// 结果: 正确
str = lfuCache.get(3);
StdOut.println("get cache from lfucache: key=3, value = " + str);
// 预期:
// [frequency = 1]->[ [key = 4, value = 4]]
// [frequency = 2]->[ [key = 3, value = 3]]
// 实际:
// {frequency=1}LfuCacheNode{frequency=1, key=4, value=4}
// {frequency=2}LfuCacheNode{frequency=2, key=3, value=3}
// 结果: 正确
lfuCache.set(4, "4");
// 预期: 返回空,结构不变
str = lfuCache.get(1);
Assert.assertNull(str);
StdOut.println("get cache from lfucache: key=1, value = null");
// 预期:
// [frequency = 1]->[ [key = 4, value = 4]]
// [frequency = 3]->[ [key = 3, value = 3]]
// 实际:
// {frequency=1}LfuCacheNode{frequency=1, key=4, value=4}
// {frequency=3}LfuCacheNode{frequency=3, key=3, value=3}
// 结果: 正确
str = lfuCache.get(3);
Assert.assertEquals("3", str);
StdOut.println("get cache from lfucache: key=3, value = " + str);
// 预期:
// [frequency = 2]->[ [key = 4, value = 4]]
// [frequency = 3]->[ [key = 3, value = 3]]
// 实际:
// {frequency=2}LfuCacheNode{frequency=2, key=4, value=4}
// {frequency=3}LfuCacheNode{frequency=3, key=3, value=3}
// 结果: 正确
str = lfuCache.get(4);
StdOut.println("get cache from lfucache: key=4, value = " + str);
}
@Test
public void testNormalSet() {
lfuCache.set(1, "1");
Assert.assertEquals(1, lfuCache.size());
}
@Test
public void testNormalGet() {
String str = lfuCache.get(1);
Assert.assertNull(str);
}
@Test
public void testNormalSetAndGet() {
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++) {
lfuCache.set(i, "" + i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++) {
String val = lfuCache.get(i);
StdOut.println("Key: " + i + ", value: " + lfuCache.get(i));
Assert.assertEquals("" + i, val);
}
}
@Test
public void testRemoveFrontByGet() {
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++) {
lfuCache.set(i, "" + i);
}
// 第一次获取key为10
// 缓存顺序应该为10,0,...
}
@Test
public void testOverrideFromEnd() {
int overrideCount = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < capacity + overrideCount; i++) {
if (capacity == i) {
StdOut.println("");
}
lfuCache.set(i, "" + i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < capacity + overrideCount; i++) {
String val = lfuCache.get(i);
StdOut.println("Key: " + i + ", value: " + lfuCache.get(i));
if (i < overrideCount) {
Assert.assertNull(val);
} else {
Assert.assertEquals("" + i, val);
}
}
}
@Test
public void testNormalParallelSetAndGet() throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(capacity * 2);
IntStream.range(0, capacity).<Runnable>mapToObj(key -> () -> {
lfuCache.set(key, UUID.randomUUID().toString());
countDownLatch.countDown();
}).forEach(executorService::execute);
IntStream.range(0, capacity).<Runnable>mapToObj(key -> () -> {
lfuCache.get(key);
countDownLatch.countDown();
}).forEach(executorService::execute);
countDownLatch.await();
StdOut.println("LruCache Size: " + lfuCache.size());
Assert.assertEquals(lfuCache.size(), capacity);
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++) {
StdOut.println("key: " + i + ", value: " + lfuCache.get(i));
}
}
@Test
public void testEvictParallelSetAndGet() throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(capacity * 2);
IntStream.range(0, capacity * 2).<Runnable>mapToObj(key -> () -> {
lfuCache.set(key, UUID.randomUUID().toString());
lfuCache.set(key, UUID.randomUUID().toString());
countDownLatch.countDown();
}).forEach(executorService::execute);
IntStream.range(capacity, capacity * 2).<Runnable>mapToObj(key -> () -> {
StdOut.println(lfuCache.get(key));
countDownLatch.countDown();
}).forEach(executorService::execute);
countDownLatch.await();
StdOut.println("LruCache Size: " + lfuCache.size());
for (int i = capacity; i < capacity * 2; i++) {
StdOut.println("key: " + i + ", value: " + lfuCache.get(i));
}
Assert.assertEquals(lfuCache.size(), capacity);
lfuCache.clear();
Assert.assertEquals(lfuCache.size(), 0);
executorService.shutdown();
}
private Object invokeMethod(String funcName, Integer key, String[] arguments) throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
Method method = null;
Method[] methods = LfuCache.class.getDeclaredMethods();
for (int j = 0; j < methods.length; j++) {
if (methods[j].getName().equals(funcName)) {
method = methods[j];
}
}
if (method == null) {
return null;
}
Object ret = null;
if (method.getParameterCount() > 1) {
ret = method.invoke(lfuCache, key, arguments[1]);
} else {
ret = method.invoke(lfuCache, key);
}
if (method.getReturnType().getName().equals("void")) {
ret = null;
}
return ret;
}
}
6、总结
- 双向链表需要自己编写,不能使用Java提供的LinkedList,当缓存节点计数增加需要将从当前计数链表中删除时Java提供的LinkedList需要O(n)的时间。
- 对缓存数据建立哈希索引是非常关键的步骤,大大提升了查找效率
7、参考
LFU缓存算法及Java实现